 HIP-367: Unlimited Token Associations Per Account
HIP-367: Unlimited Token Associations Per Account
| Author | Anirudh Ghanta |
|---|---|
| Working Group | Richard Bair, Jasper Potts, Michael Tinker, Anirudh Ghanta |
| Discussions-To | https://github.com/hashgraph/hedera-improvement-proposal/discussions/380 |
| Status | Final ⓘ |
| Needs Council Approval | Yes ⓘ |
| Review period ends ⓘ | Mon, 11 Apr 2022 07:00:00 +0000 |
| Type | Standards Track ⓘ |
| Category | Service ⓘ |
| Created | 2022-02-17 |
| Updated | 2022-09-08 |
| Release | v0.25.0 |
Table of Contents
- Abstract
- Motivation
- User stories
- 1. A User can associate with 1,001 tokens
- 2. A User can configure auto association to more than 1,000
- 3. An NFT Creator can mint thousands of NFTs in a single collection
- 4. A secondary NFT Marketplace dApp can have thousands of collections
- 5. A User can get the full set of tokens and balances from the mirror node
- 6. A User can delete an account with associated tokens if there are no balances
- 7. A User’s account has expired while they have associated tokens with balances
- Specification
- Backwards Compatibility
- Security Implications
- How to Teach This
- Reference Implementation
- Rejected Ideas
- Open Issues
- References
- Copyright/license
Abstract
Permits every account to hold an unlimited number of token associations. Retains the current pricing for each token
association. Deprecates the return of token associations from the getAccountInfo, getContractInfo, and
getAccountBalance queries and modifies the specification of the returned results during the deprecation period.
Changes the criteria for the cryptoDelete transaction to require all token balances to be zero before successfully
marking the account as deleted.
Motivation
The current Services API permits the user to have at most 1,000 token associations per account. This limitation was
imposed because the current implementation becomes prohibitively expensive with large numbers of associations. In
addition, processing and returning the getAccountBalance query becomes more expensive linearly as the number of
associations increases. A user can work around this limitation by creating multiple accounts, each of which is also
limited to 1,000 token associations, but several use cases become difficult or awkward to support in this way.
User stories
1. A User can associate with 1,001 tokens
I have an account with 1,000 tokens already associated with it. After the update to the release with the limit removed, I can add another token association, putting my account at 1,001 associations.
2. A User can configure auto association to more than 1,000
I am a user who loves receiving airdrops. I configure my account to have 10,000 “slots” for auto associated tokens. I pay for all these up front. I can then actually receive up to 10,000 auto associated tokens. An attempt to send me a 10,001st auto associated token would fail, but if I manually associated a 10,001st token, it would succeed.
I can only auto-associate a maximum of 2^(32-1) tokens (a little more than 2.15 billion).
3. An NFT Creator can mint thousands of NFTs in a single collection
I love creating NFTs. As a primary creator of an NFT collection, I am able to mint thousands of NFT serials in a single collection.
4. A secondary NFT Marketplace dApp can have thousands of collections
As a secondary NFT marketplace dApp, I should be able to create thousands of collections (created by multiple primary creators of the collections), such that each collection can hold thousands of NFTs.
5. A User can get the full set of tokens and balances from the mirror node
I have a large collection of thousands of tokens. I can query a mirror node to get the full set of tokens and their current balances.
6. A User can delete an account with associated tokens if there are no balances
I have thousands of token associations. Several thousand of these were manually associated and several thousand were auto-associated. But none of them have any balance. I can delete my account.
7. A User’s account has expired while they have associated tokens with balances
I have an account with tens of thousands of associated tokens and some of those tokens have balances. But I no
longer want this account, and it has no HBAR in it, and I let it expire. The system will clean this up for me.
Specification
Consensus Nodes
Current Implementation
The current implementation of token associations involves several data structures stored in the merkle tree.
There is a MerkleAccount node in the tree for each account. It has three leaf nodes hanging off it, two of which
are MerkleAccountState and MerkleAccountTokens. The MerkleAccountState contains information like the key,
hbarBalance, and other information about the account. The MerkleAccountTokens is an array of token IDs, one for
each token that is associated with the account. The more tokens associated with the account, the larger the array.
Every time a new token association is made, it is added to the array, the array is sorted, and the entire array is
hashed. Every time a token association is removed, we walk the array to find the token ID and remove it from the array,
and the array is hashed. When we query for the account balance, then for each token ID in the array we make a separate
map lookup in tokenAssociations to get the balance.
Separate from accounts is the tokenAssociations map in the merkle tree. This maps from EntityNumPair (the pair
of account ID and token ID) to MerkleTokenRelStatus. It is this MerkleTokenRelStatus that contains information
for the association, such as the balance or whether it was an automaticAssociation.
An unbounded array of associations per account is undesirable with this design because the amount of time it takes to
hash the MerkleAccountTokens leaf becomes excessive as the number of associations grows, and any state proof involving
that leaf requires passing the entire array along, making the state proof very large. It also means the
getAccountBalance query becomes arbitrarily expensive since it requires reading a MerkleTokenRelStatus from
tokenAssociations for each token ID in the account’s MerkleAccountTokens array!
Thus, we set the boostrap property tokens.maxPerAccount to 1000 in testnet and mainnet to limit the maximum number of
associations per account.
Enforcing the limit
HederaTokenStore.associate is called when auto-associating an account with a token during a token transfer. In this
method we verify that the new auto association will not increase the number of tokens for this account past the limit
defined by tokens.maxPerAccount.
Account.associateWith is called when manually associating with a TokenAssociate transaction. In this method we also
verify that the account does not get associated with more tokens than specified by tokens.maxPerAccount.
We also verify that the value for maxAutomaticAssociations on the account (as described by
HIP-23) does not exceed
tokens.maxPerAccount.
New Implementation
The weakness in the current design is in the MerkleAccountTokens. Rather than having an array of token IDs in the
account state and a map of token associations, we will modify the tokenAssociations map to be combination map and
linked list. Each MerkleTokenRelStatus will have a prev and next containing the token ID of the
previous association and the next association. The previous association must be 0 if the MerkleTokenRelStatus
represents the first in the list for the account, and the next association must be 0 if the MerkleTokenRelStatus
is the last in the list for the account.
Thus, to follow the chain, you start at the first MerkleTokenRelStatus for the account, and follow the next
links one after another. For each, you create a temporary EntityNumPair with the account ID and the token ID
contained in next to look up the next entry in the list. The prev link exists to allow us to efficiently
delete an item from the list, as with any standard doubly-linked-list implementation.
The MerkleAccountState will receive a new fields, integer numPositiveBalances, another integer numAssociations,
and one long, headTokenId. The linked list always pushes the most recent addition to the head of the list,
referred to by headTokenId. Walking the list from first to last would list the tokens in order from most recently
added to the least recently added to the list (however, due to migration, the position in the list
may not be ordered by when the token was associated).
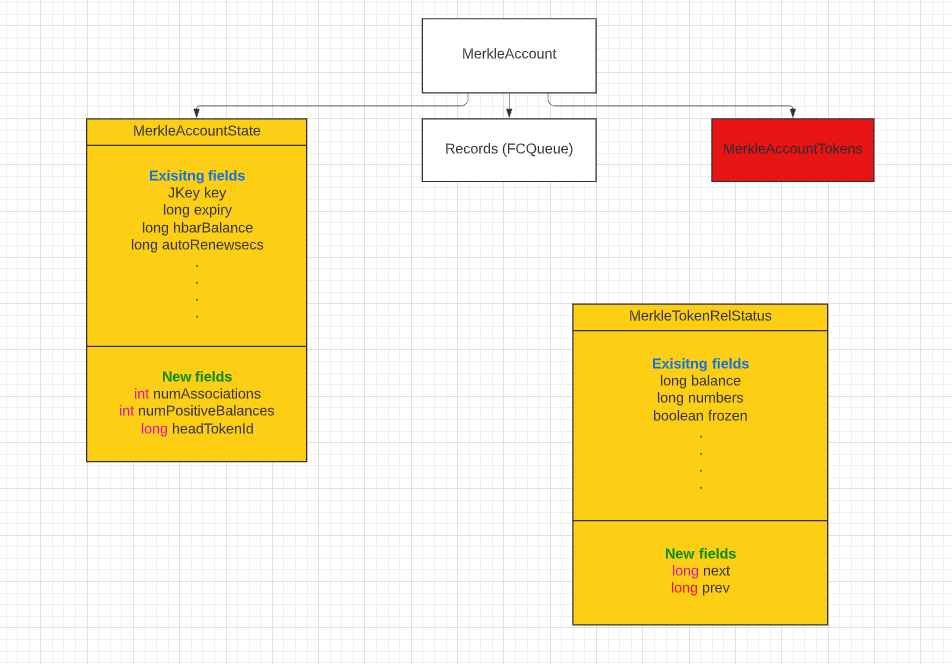 TODO Image needs to be updated to include new / proper names
TODO Image needs to be updated to include new / proper names
The headTokenId is updated whenever a new token associates with the account (either explicitly or through auto
associations), or when the first association is removed, or during migration.
The numPositiveBalances field is updated whenever one of the balances of the token list for the account is changed
from being a zero balance to a non-zero balance or vice-versa. This can happen:
tokenWipeoperation is performed with the account’s token balance becoming zerotokenBurnoperation is performed with treasury’s balance becoming zerotokenMintoperation is performed with treasury balance becoming non-zerocryptoTransferwhere either sender or receiver balances toggle between zero and non-zero
When a user tries to delete an account, if numPositiveBalances is greater than 0, then we will not allow the account
to be deleted. The user must first transfer balances out for all tokens.
The numAssociations field is needed so we can efficiently compute a renewal price.
Migration
During migration, nodes will load an older state containing MerkleAccountTokens. We will continue to host this leaf
until migration completes, after which we will remove it. During migration, we will iterate over all accounts. For each
account, we will iterate over each token ID in MerkleAccountTokens. For each token ID, we will construct an
EntityNumPair from the account ID and token ID and look up the associated MerkleTokenRelStatus. The first token ID
we handle will become the end of the list. So for each subsequent token ID we handle, it will become the prev of
the previous MerkleTokenRelStatus. The very last token ID will be the headTokenId for the account.
- For each account in the accounts map fetch the list of token IDs from
MerkleAccountTokens - For each token on this list, use the account id and token id to build
EntityNumPairand fetch theMerkleTokenRelStatusfrom thetokenAssociationsmap. - Update the
nextandprevfor each of these associations and persist the changes - If the balance on the association is non-zero, then increment the
numPositiveBalanceson the account by 1. - Set the account’s
headTokenIdto the last token ID from the above loop - Finally, remove the
MerkleAccountTokensfrom the account
Token Association
Token association can occur either explicitly or automatically. In either case, the same algorithm is used, except
that in the case of automatic association we validate that maxAutomaticAssociations will not be exceeded by this
association. Management of alreadyUsedAutomaticAssociations remains as it does today and is not altered by this HIP.
- For each token that is to be associated to the Account, build an
EntityNumPairfrom the token ID and account ID - Create a new
MerkleTokenRelStatusobject and set thenextas the currentheadTokenId - Update the account’s
headTokenIdto the new token ID - Persist all created or modified
MerkleTokenRelStatusobjects and the account.
Token Dissociation
Token disassociation requires maintenance of the linked list. Management of alreadyUsedAutomaticAssociations remains
as it does today and is not altered by this HIP.
- Look up the
MerkleTokenRelStatusfor the token ID we are removing. We will call it theremovedEntry - If the balance on the token association is not 0, then fail
- Remove
removedEntryfromtokenAssocations - If
removedEntry.tokenIdisheadTokenIdthen:- If
numAssociationsis 1 then this was the last association. SetheadTokenIdto0. - Else look up the
MerkleTokenRelStatusforremovedEntry.nextand call itnextEntry. SetnextEntry.prevto0and setheadTokenIdtonextEntry.tokenId
- If
- Else get the
MerkleTokenRelStatusforremovedEntry.nextcallednextEntryand theMerkleTokenRelStatusforremovedEntry.prevcalledprevEntry. SetprevEntry.nexttonextEntry.tokenIdandnextEntry.prevtoprevEntry.tokenId - Decrement
numAssociationsby 1. - Persist all updated
MerkleTokenRelStatusobjects and the account.
Association lists in query responses
Three queries return token association data: getAccountInfo, getAccountInfo, and getAccountBalance.
This HIP formally deprecates the token association lists returned by these three queries. Within 6 months this information will no longer be retrieved from consensus nodes. Instead, clients must query mirror nodes for this information.
Please follow this issue to track progress on the Mirror Node replacement API.
The challenge with these queries is that they require numerous uncharged map look-ups to find and retrieve the
token information, and when token limits are removed, these queries may take an arbitrary amount of time to complete.
For this reason, and to maintain compatibility during the deprecation period, we will continue to return at most
1000 (tokens.maxRelsPerInfoQuery) results. The order of these results is explicitly not specified. Thus, if you
have 1001 token associations, we will only return 1,000 of them, and are free to return any 1,000. Instead, clients are
strongly encouraged to query this information from mirror nodes.
- Get the latest token association from the account’s
headTokenId - Fetch the
MerkleTokenRelStatususing the combination of the account ID and token ID fromtokenAssociations - Add the token information to the list of information to return from the query
- Get the
nexttoken ID from thisMerkleTokenRelStatusobject and repeat step 2 and 3 until thenextequals0which means we reached the end of the linked list, or until we reach the limit specified bytokens.maxRelsPerInfoQuery.
CryptoTransfer
When transferring any token units (Fungible or Non-Fungible) we have to update the numPositiveBalances on each of
those accounts respectively.
On every tryAdjustment and updateLedgers calls when adjusting token units:
- If the sender is left with no more token units, then decrement the
numPositiveBalancesby 1 - If the receiver’s initial balance for this token type is 0, then increment the
numPositiveBalancesby 1.
TokenWipe
When a TokenWipe operation is performed on an account, we have to update the numPositiveBalances accordingly. When
wiping either Fungible token units or NFT units on an account:
- If the remaining units on that token for that account is 0, then decrement the
numPositiveBalancesby 1.
TokenBurn
When a TokenBurn operation is performed, we burn the asked amount off the treasury account and update the total supply.
Update the numPositiveBalances of the treasury if the burn left the treasury with zero balance on that token. When
burning either Fungible token units or NFT units of a token:
- If the treasury has no more units left, then decrement the
numPositiveBalancesby 1.
TokenMint
When a TokenMint operation is performed, we mint the asked amount of token units, by adding to the treasury account’s
token balance, and we update the total supply of that token. We increment the numPositiveBalances of the treasury if
the original balance for treasury on that token is 0. When minting either Fungible token units or NFT units of a token:
- If the treasury has 0 units of that token before minting, then increment the
numPositiveBalancesby 1.
Crypto Account Deletion
Currently, we return TRANSACTION_REQUIRES_ZERO_TOKEN_BALANCES when a cryptoDelete transaction is submitted on an
account with non-zero balances on the tokens [ not deleted] that it is associated with.
Checking if the associated token is not deleted and then validating the balance on that association gets very costly
when the association limit is removed as we would have to traverse the whole list of associations. Instead, we will
include the deleted tokens as well when checking if the account has any non-zero token balances and use the field
numPositiveBalances to match if all the associations have zero balances so that we can avoid traversing the list of
unlimited token associations.
An account must dissociate from deleted tokens if it has any token balances left pertaining to that token to be eligible for deletion
Balance exporter
Balance exporter would need all the token associations without the limitation enforced by tokens.maxPerAccount.
AutoRenew
AutoRenew fee calculations require the numAssociations on the renewing account.
Mirror Node
Accounts REST API
The /api/v1/accounts and /api/v1/accounts/{id} REST APIs will remain unchanged except limits will be put in place
on the nested list of token balances. This will ensure that the token data returned won’t grow unbounded and increase
API response times. Currently /api/v1/accounts/{id} will be limited to 1000 token balances in its response and
/api/v1/accounts will be limited to at most 50 token balances per account. These limits may be adjusted as
necessary in the future to ensure API stability. Users should use the new Token Relationships REST API
to retrieve more tokens than the limits provide.
Balances REST API
For the same reasons as the accounts REST API, the /api/v1/balances API will limit the nested list of token balances
to at most 50 token balances per account. Users should use the new Token Relationships REST API
to retrieve more tokens than the limits provide.
Token Relationships REST API
A new /api/v1/accounts/{id}/tokens REST API will be added
to show the tokens associated with a specific account ID.
{
"tokens": [{
"automatic_association": true,
"balance": 5,
"created_timestamp": "123456789.000000001",
"freeze_status": "UNFROZEN",
"kyc_status": "GRANTED",
"symbol": "F",
"token_id": "0.0.27335"
}],
"links": {
"next": null
}
}
It will support the following query parameters:
limit- The maximum number of results to return. Defaults to 25 and max 100 allowed.order- Sort by token ID. Value ofascordescwith a default ofasc.token.id- The token IDs to filter by. Supportseq,gt,gte,lt,lteoperators. Used for pagination in next link.
Backwards Compatibility
There are two functional changes required by this move to unlimited token associations.
First, when an account has more than 1000 tokens associated to it, the getAccountInfo, getContractInfo,
and getAccountBalance queries will not support fetching all of those associations. Rather the number of token
associations that will be fetched from the queries will be dictated by the dynamic property
tokens.maxRelsPerInfoQuery. The token associations returned by these queries will have at most 1000
associations. They may come in any particular order. (As noted above, this HIP officially deprecates the
token association data in these three queries. Clients should plan migration strategies to begin getting
this information from mirror nodes, c.f. this issue.)
Second, accounts can no longer deleted via a CryptoDelete while holding units of any token type, even if that
token type is deleted. All balances must be cleared before deletion.
Security Implications
With the removal of the limit on number of token associations on an account, an account can potentially have millions of token associations. We must be sure that all code paths are ready to deal with millions of associations in the list and do not expose us to a DOS attack.
How to Teach This
N/A
Reference Implementation
Rejected Ideas
- Users can create multiple accounts and hold 1000 tokens in each
- Users can create a smart contract and manage around the current 1000 token limit by creating multiple accounts each with 1000 tokens and use smart contract logic to manage the mapping
- Users can opt to create tokens on the EVM layer, which is not subjected to the 1000 token limit but this doesn’t use Hedera’s native tokenization
- Create an
exchange-accounttype of account where we charge more to create, but they have a higher association limit
Open Issues
MapValueLinkedList
Increase token association limit
HIP - 367 : Remove limit on the number of tokens that can be associated to an account
Services-PR
References
N/A
Copyright/license
This document is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 – see LICENSE or (https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0)
Citation
Please cite this document as: